Geographical concepts in Thailand
When filling in forms, it does happen that a number of geographical terms are used, the meaning of which is not immediately clear. It often refers to the living environment of the person who has to fill in the form.
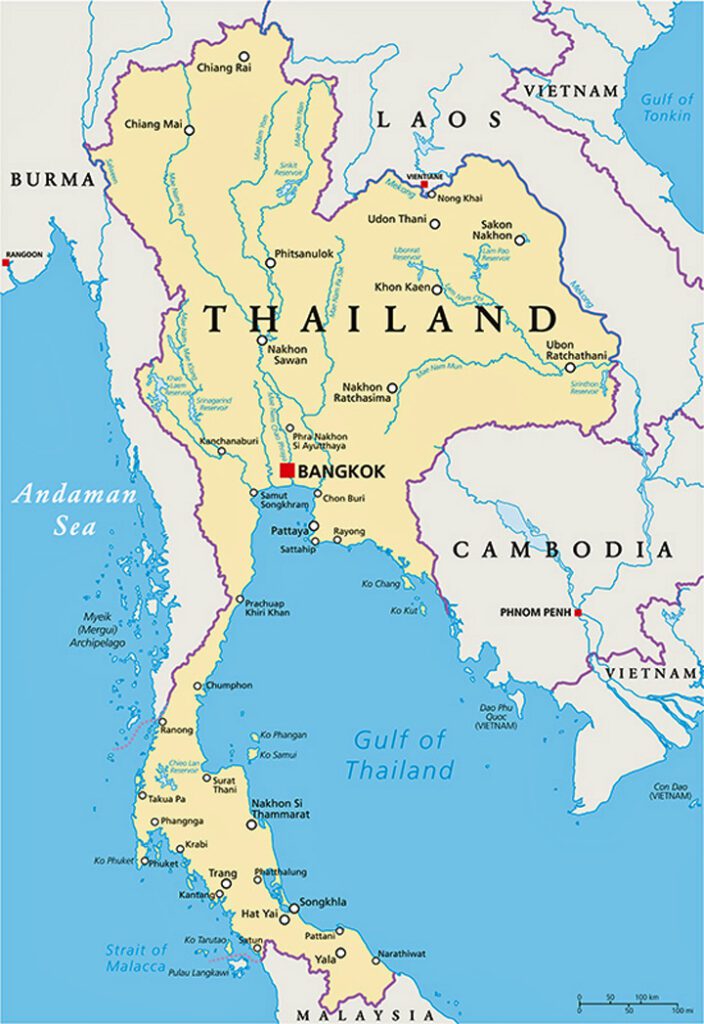
- Thailand, like many other countries, has provinces changwat named. The country has 76 provinces, but I wouldn't be surprised if this number has changed again.
- Each province is subdivided into districts amphoe.
- These districts are in turn subdivided into municipalities, the so-called tambon.
- But such a municipality has a number of villages, which moo job to be named
Each province has a capital with the same name. But in order not to create confusion, the word mueang is placed before the name of the city. The capital is the largest city in the province except Songkhla province, where the city of Hat Yai is larger. The provinces are governed by a governor, except in Bangkok where the "Governor of Bangkok" is elected. Although Bangkok province has the largest population size in terms of population density, Nakhon Ratchasima (Korat) is Thailand's largest province.
As in the Netherlands, the former provinces were independent sultanates, kingdoms or principalities. Later these were absorbed into larger Thai kingdoms such as the Ayutthaya kingdom. The provinces were created around a central city. These provinces were often governed by governors. These had to work on their own income through taxes and send an annual tribute to the king.
It was not until 1892 that administrative reforms took place under King Chulalongkorn and ministries were reorganized according to a Western system. So it happened that in 1894 Prince Damrong became the Minister of the Interior and was therefore responsible for the administration of all provinces. That people did not agree in a number of places due to loss of power, was shown by the "The holy man" revolt in Isan in 1902. The revolt started with a sect that proclaimed that the end of the world had come and even the place Khemarat was completely destroyed in the process. After a few months, the uprising was crushed.
When Prince Damrong abdicated in 1915, the entire country was organized into 72 provinces.
Source: Wikipedia


Are you sure "moobaan" refers to a village? I see all village names start with 'ban'.
Ban is written in Thai as บ้าน and pronounced as with a long falling A sound. Moobaan (หมู่บ้าน) is the actual translation of village and all villages have a number in addition to their name, which comes after the word 'moo', such as หมู่ 1, หมู่ 2 etc.
หมู่ mòe: (long -oe- and low tone) means group. It can also be a group of people, islands, stars and blood type. บ้าน bâan (long –aa- and falling tone) is of course 'house'. Together 'a group of houses', a village. But job also means more than just house: place, home, with the intimate meaning of 'I, we, us'. Bâan meuang' is for example 'country, nation', Bâan kèut is 'birthplace'.
Moo Baan means group of houses. A small village is therefore usually called a Moo Baan. A larger place (city for example) is often a collection of several Moo Baans, in fact residential areas, as you also see in Bangkok.
Indeed, the name of many villages often starts with the word Baan. That is often the name of the founder of that village. Eg, Moobaanbaan Mai, is a village calledbaan mai. That village was probably founded by someone named Mai. There is also a village called Baan Song Pi Nong, founded by two brothers or sisters.
บ้าน [job] = house (can also be village)
หมู่บ้าน [tired job] = village
But depending on where a letter is, the pronunciation sometimes changes. This is known in Dutch, but also in Thai. If บ้าน is in front, the pronunciation changes.
An easier example is น้ำ (water/liquid) pronunciation is [name]. But น้ำแข็ง (water+hard, ice) is [namkeng]. And น้ำผึ้ง (water+bee, honey) is [namphung]. Or น้ำรัก, [namrak], you can find out for yourself what that is. 555
See:
http://thai-language.com/id/131182
http://thai-language.com/id/199540
http://thai-language.com/id/131639
Rob, job means home, but never village, without the word Moo before it.
Unclear what you mean by a different statement and your example of it. นำ้ (meaning water without addition) is always pronounced the same. I think you mean that the word following นำ้ can change the meaning to eg juice, as นำ้ส้ม (literally: water orange) translates to orange juice.
Thanks for the addition Peter. I learned from thai-language.com that it can also mean village:
บ้าน jobF
1) house; home; place (or one's place); village
2) home plate (baseball)
3) [is] domestic; domesticated
In colloquial terms, you and thai-language.com may be right that Baan can also mean village. I've never come across that meaning myself. I think it is laziness rather than correctness on the part of the speaker.
Thai is actually very simple. It has no plural. Job is house and Moo job is group of houses. The plural is made clear with the word Moo in front, or for example “sip lang” after it.
I have to agree with Rob, dear Peter. Name, water, is pronounced with a long -aa- and a high tone, but only in civilized, standard Thai. All Thai dialects say nam with a short -a- and also a high tone.
But in combinations like น้ำแแข็ง nám khǎeng ice, and , น้ำมัน nám man gasoline, fuel is not name but name.
sorry but the Wikipedia explanation is not entirely correct Because people forget the Tessaban, and in the Province of Bangkok there are no Amphur but Khet0 and there are still a few inaccuracies
Indeed BKK is the only one divided into 50 khets = city parts / districts.
There is also the BMA, a kind of city region, which, in addition to BKK, includes Nonthburi, and parts of Patum Thanee and Samut Prakarn. The BMTA provides bus transport here.
Finally, a number of chiangwats are more or less officially subdivided into cardinal regions: North/North-East (=Isan), East, South and Central.
Provinces are indeed subdivided into districts, the Ampurs. The Amphur is in fact the municipality, and the Tambon (sub district) a part of it.
I'm looking for a map with all districts (readable, so not in Thai) of Nonthaburi, any tips?
After the new province of Bueng Kan was separated from Nong Khai, Thailand now has – if I remember correctly – 77 provinces.